在日常项目开发中,单例模式可以说是最常用到的设计模式,项目也常常在单例模式中需要使用 Service 逻辑层的方法来实现某些功能。通常可能会使用 @Resource 或者 @Autowired 来自动注入实例,然而这种方法在单例模式中却会出现 NullPointException 的问题。那么本篇就此问题做一下研究。
演示代码地址
问题初探 一般我们的项目是分层开发的,最经典的可能就是下面这种结构:
1 2 3 ├── UserDao -- DAO 层,负责和数据源交互,获取数据。 ├── UserService -- 服务逻辑层,负责业务逻辑实现。 └── UserController -- 控制层,负责提供与外界交互的接口。
此时需要一个单例对象,此对象需要 UserService 来提供用户服务。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Slf4j public class UserSingleton { private static volatile UserSingleton INSTANCE; @Resource private UserService userService; public static UserSingleton getInstance () { if (null == INSTANCE) { synchronized (UserSingleton.class) { if (null == INSTANCE) { INSTANCE = new UserSingleton (); } } } return INSTANCE; } public String getUser () { if (null == userService) { log.debug("UserSingleton userService is null" ); return "UserSingleton Exception: userService is null" ; } return userService.getUser(); } }
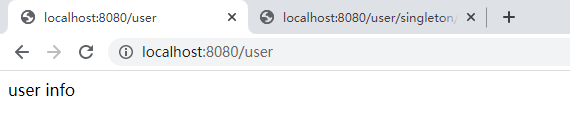
然后创建一个 UserController 来调用 UserSingleton.getUser() 方法看看返回数据是什么。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @RestController public class UserController { @Resource private UserService userService; @GetMapping("/user") public String getUser () { return userService.getUser(); } @GetMapping("/user/singleton/ioc") public String getUserFromSingletonForIoc () { return UserSingleton.getInstance().getUser(); } }
可以看到,在 UserController 中自动注入 UserService 是可以正常获取到数据的。
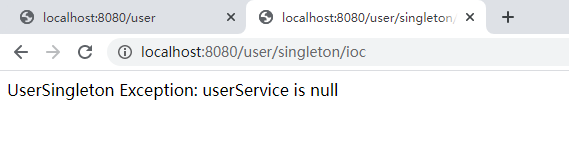
但是如果使用在单例模式中使用自动注入的话,UserService 是一个空的对象。
所以使用 @Resource 或者 @Autowired 注解的方式在单例中获取 UserService 的对象实例是不行的。如果没有做空值判断,会报 NullPointException 异常。
问题产生原因 之所以在单例模式中无法使用自动依赖注入,是因为单例对象使用 static 标记,INSTANCE 是一个静态对象,而静态对象的加载是要优先于 Spring 容器的。所以在这里无法使用自动依赖注入。
问题解决方法 解决这种问题,其实也很简单,只要不使用自动依赖注入就好了,在 new UserSingleton() 初始化对象的时候,手动实例化 UserService 就可以了嘛。但是这种方法可能会有一个坑,或者说只能在某些情况下可以实现。先看代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @Slf4j public class UserSingleton { private static volatile UserSingleton INSTANCE; @Resource private UserService userService; private UserService userServiceForNew; private UserSingleton () { userServiceForNew = new UserServiceImpl (); } public static UserSingleton getInstance () { if (null == INSTANCE) { synchronized (UserSingleton.class) { if (null == INSTANCE) { INSTANCE = new UserSingleton (); } } } return INSTANCE; } public String getUser () { if (null == userService) { log.debug("UserSingleton userService is null" ); return "UserSingleton Exception: userService is null" ; } return userService.getUser(); } public String getUserForNew () { if (null == userServiceForNew) { log.debug("UserSingleton userService is null" ); return "UserSingleton Exception: userService is null" ; } return userServiceForNew.getUser(); } }
下面是 UserService 的代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public interface UserService { String getUser () ; String getUserForDao () ; } @Slf4j @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Resource private UserDao userDao; @Override public String getUser () { return "user info" ; } @Override public String getUserForDao () { if (null == userDao){ log.debug("UserServiceImpl Exception: userDao is null" ); return "UserServiceImpl Exception: userDao is null" ; } return userDao.select(); } }
创建一个 UserController 调用单例中的方法做下验证。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @RestController public class UserController { @Resource private UserService userService; @GetMapping("/user") public String getUser () { return userService.getUser(); } @GetMapping("/user/singleton/ioc") public String getUserFromSingletonForIoc () { return UserSingleton.getInstance().getUser(); } @GetMapping("/user/singleton/new") public String getUserFromSingletonForNew () { return UserSingleton.getInstance().getUserForNew(); } @GetMapping("/user/singleton/new/dao") public String getUserFromSingletonForNewFromDao () { return UserSingleton.getInstance().getUserForNewFromDao(); } }
通过上面的代码,可以发现,通过手动实例化的方式是可以一定程度上解决问题的。但是当 UserService 中也使用自动依赖注入,比如 @Resource private UserDao userDao;,并且单例中使用的方法有用到 userDao 就会发现 userDao 是个空的对象。
也就是说虽然在单例对象中手动实例化了 UserService ,但 UserService 中的 UserDao 却无法自动注入。其原因其实与单例中无法自动注入 UserService 是一样的。所以说这种方法只能一定程度上解决问题。
最终解决方案 我们可以创建一个工具类实现 ApplicationContextAware 接口,用来获取 ApplicationContext 上下文对象,然后通过 ApplicationContext.getBean() 来动态的获取实例。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component public class SpringContextUtils implements ApplicationContextAware { private static ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public void setApplicationContext (ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { SpringContextUtils.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext () { return applicationContext; } public static Object getBean (String name) { return applicationContext.getBean(name); } public static <T> T getBean (Class<T> clazz) { return applicationContext.getBean(clazz); } public static <T> T getBean (String name, Class<T> clazz) { return applicationContext.getBean(name, clazz); } }
然后改造下我们的单例对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 @Slf4j public class UserSingleton { private static volatile UserSingleton INSTANCE; private UserService userServiceForTool; private UserSingleton () { userServiceForTool = SpringContextUtils.getBean(UserService.class); } public static UserSingleton getInstance () { if (null == INSTANCE) { synchronized (UserSingleton.class) { if (null == INSTANCE) { INSTANCE = new UserSingleton (); } } } return INSTANCE; } public String getUserForToolFromDao () { if (null == userServiceForTool) { log.debug("UserSingleton userService is null" ); return "UserSingleton Exception: userService is null" ; } return userServiceForTool.getUserForDao(); } }
在 UserController 中进行测试,看一下结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @RestController public class UserController { @GetMapping("/user/singleton/tool/dao") public String getUserFromSingletonForToolFromDao () { return UserSingleton.getInstance().getUserForToolFromDao(); } }
访问接口,返回结果是:user info for dao,验证通过。
其他 本文源码地址
欢迎关注本人 github 中的 spring-boot-example 和 spring-cloud-example 项目,为您提供更多的 spring boot 及 spring cloud 教程及样例代码。博主会在空闲时间持续更新相关的文档。
spring-boot-example
spring-cloud-example